Difference between revisions of "Cahbacan"
From EncyclopAtys
m |
|||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
{{Last version link|Cahbacan}} | {{Last version link|Cahbacan}} | ||
| − | {{Portal|Flora | + | {{Portal|Flora}} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | }} | ||
[[Category:Flora]] | [[Category:Flora]] | ||
[[Category:Aquaplants]] | [[Category:Aquaplants]] | ||
[[Category:Fungi]] | [[Category:Fungi]] | ||
[[Category:Flora of the Lakes]] | [[Category:Flora of the Lakes]] | ||
Revision as of 15:57, 9 November 2019
Page proposed to the Lore of Ryzom
Latest edition: Lanstiril, 09.11.2019
| Taxonomic Amber | |
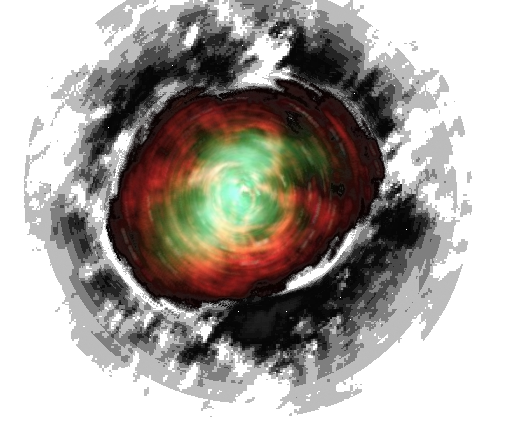
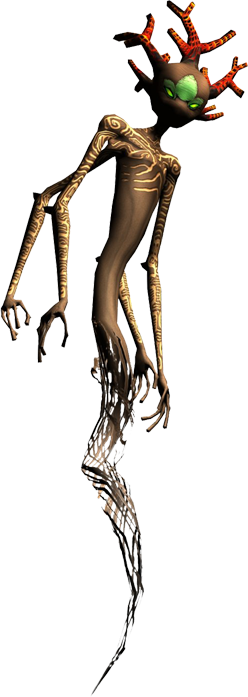
| Cahbacan in springtime | |
|---|---|

| |
| Kingdom | Plants |
| Category | Aquaplant & Fungus |
| Main Ecosystem(s) | Lakes |
| Counterattack type | None |
Also known as "mushfloat", the cahbacan is a plant of the same family as the sailtree. Of very different appearance, it looks like a large floating mushroom.
These plants are important recycling agents for the water of the lakes.
Although the outer casing of its head is harder than that of a mushroom, the inside is filled with a similar spongy, very light, flesh.
Once treated with a varnish of manhart roots, this material is used to manufacture floats and build non-load-bearing arches.
Last version 2019-11-10•ᐒ