At the invitation of Namcha (Lore Team), several players gathered on the evening of 13 August 2021 at the Thesos Research Centre to learn more about Atys and its sky.
The distances
In game, the compass tells you how far your character is from a creature or character you are targeting. It also tells you the distance to any place of Atys when, on the map displayed (key M), you click on the flag that indicates the place in question. But in this case, the distance is wrong. Indeed, for long distances (greater than the maximum distance for direct targeting), the compass is not realistic: the New Lands are a bit larger than they seem!
The real distance, between two cities for example, must in fact be calculated from the Atysian time taken by your character to actually cover it in a straight line, which can be calculated from the clock displayed on the map. However, multiplying the distance indicated by the compass by 20 is a good approximation of this real distance within each country (country = area delimited by vortices), but not between countries.
This being said, the New Lands cover an area of about 120,000 km² (a square of 300 to 350 km on each side), which is still quite small, much smaller than the Old Lands in any case. Let's remember that what we call New Lands is the set of countries mapped by the in-game maps, countries that the homins have joined after the Great Swarming. In fact, since the beginning of the game, the homins live on these New Lands and only know about the Old Lands, which are not mapped, what the texts say of them.
But let's go back to the question of using the compass to evaluate the distance between countries. Indeed, with the compass you can play the funny game of triangulating positions to obtain a "server map" which is very different from the map displayed in game. The fact remains that it is the latter that is the authentic one for the story: the "server map" is just computer science. Or if it had a meaning, it has long since been lost by the developers who succeeded one another on Ryzom.
- Q: So the countries are correctly positioned on the map?
- A: Yes. Except that the map is a "split" view, like an orange peel that you would have opened up, which also shows the countries under the Bark, the Primes Roots, which are under the New Lands.
- Q: You talk about a square of 300 to 350 km on each side, but the northern edge of the Desert seems to be only 80 km long. So there would be a large distance "hidden" by the vortices?
- A: Yes, and also some of the surrounding areas, like the old newbie islands, your guild islands, etc. It's all "around here".
- Q: OK, the countries are not really stuck together. There's some sort of buffer zone is'nt it?
- A: The vortices do make a small jump, yes. But not hundreds of miles.
- Q: So from the southwestern Desert to the Witherings, it's not that far?
- A: No. In fact, you could say that, on a planetary scale, the New Lands are very close together.
- Q: Does this mean that there are still unexplored countries around the known countries?
- A: Yes, a lot, in fact. However, it is normal that homins do not venture too far.
- Q: But... are Almati Wood, the Nexus and Silan part of the New Lands?
- A: Yes, although I know that, as for those, some rumors have it that they are not, as the Powers have said homins that they are part of the Old Lands. These places were indeed "opened" during the Temple War, by the Powers.
Astronomy
If the sky is not at all coherent in game, the celestial objects that we see there do exist in history. There are four of them and, since night has just fallen, I will review them before describing their interactions.
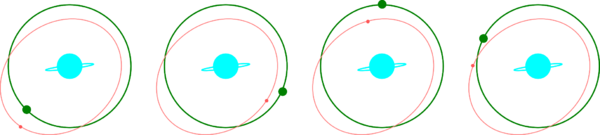
― Let's look to the east. A nebula is rising there, it will soon be at its zenith. This celestial body is the star of the Atysian system, its center. It is a sun then, but which radiates very little in the visible spectrum. Moreover, it is veiled by a cloud of celestial dust.
― To the north, we have a magnificent planet with a ring. It is a gas giant, it revolves around the star (normally). And Atys is a satellite of this gas giant that the gaming community has named “Sagaritis”.
― To the southwest, we see a “red moon”. It is moving southwards (I remind you that the movements in game are completely wrong). It orbits Sagaritis, like Atys, but with a more elliptical orbit. It is always full and it emits its own light, weak.
― Last of the list of four, the one that does not move, in the east. It is the only star that is "correct" in game: indeed, it should not move.It is the star that makes the day, the “luminary”. It is a satellite of Atys, geostationary. And, as scholars know, in the Ancient Lands, this star is at the zenith, upright.
- Q: There is one thing I don't understand. If it is geostationary and makes the day, shouldn't night never fall?
- A: No. Because it pulses. It turns on, it turns off. During the night we see the afterglow.
Atys, I said, is a satellite of Sagaritis, the gas giant planet with its ring. Atys always presents the same face to Sagaritis (it is called "synchronous rotation", like that of the Moon around the Earth). It goes around Sagaritis in one cycle, the Atysian cycle.
- Q: Does this mean that in some places on Atys, neither Sagaritis nor the pulsar can be seen? So it is always dark there?
- A: So... it's true that we could be on the wrong side of Atys and not see Sagaritis at all. And if we went far, far westward, yes, we would end up seeing the luminary no more. But... maybe something is planned to solve this problem!
- Q: The Karavan is from another planet than Atys, but is this planet in the Atysian system?
- A: No, the Karavan myth says that she comes from another world. This is why humans have the concept that there are "other worlds". The word "planet" is also part of the myth.
When the game was designed, the celestial bodies did not have names. You could almost say that they were there just to look pretty. As I said, the community named the gas giant Sagaritis (mnemonic: SAGA of RYzom, aTYS). This name, since "officially" adopted, refers to an Earth legend, of the Phrygian people (antique occupant of the present Turkey). Sagaritis is mentioned in the chronicle titled Chrysalis, which tells of the escape of Yrkanis from Jino. It was also mentioned by the player Dalcia in one of his poems. Both texts refer to the Terran legend, with nuances. That's why, to stay in this legendary reference, I propose the name of “Cybele”, or Cybel (masculine or feminine, you decide, both are acceptable) for the nebula. The legend says, roughly, that Atys is son of Cybele, and Sagaritis his lover (in Chrysalis, the genders are reversed), which carries a secret meaning for the story of the game.
And what makes the seasons on Atys, it is indeed the nebula, or Cybele. In fact Atys goes around Sagaritis, and Sagaritis goes around Cybele. For half a cycle, one should not see Cybele. When she rises, spring begins. Most of Cybele's radiation is not in the visible spectrum, but it contains enough energy to create, in addition to the luminary's, the seasons on Atys.
- Q : Is it the one who brings heat then?
- A : No. It is mainly the luminary that brings heat and light to the planet, Cybele's radiation is added to it when it is visible, that is to say present in the sky of the New Lands.
On the other hand, the light that Sagaritis sends back to us is that of Cybele. There would be a lot to say about the appearance of Sagaritis! It should be a show in its own right, throughout a cycle. It should be fixed in the sky, I already said it, but it has nothing to do in the north. The homins don't really know it, but the habitable lands, Old and New, are on the equator of Atys, at least its "equatorial belt" (don't rely too much on the image representing the planet here and there: it's an "artist's view", not a satellite photo).
Sagaritis would, if it were "correct" in game, be positioned to the west, a little higher on the horizon and, as we are in the equatorial belt of Atys, we would see its rings vertical (more or less, since Atys is not exactly in the equatorial plane of Sagaritis). So during one half of Atys' turn around Sagaritis, we would see one side of the rings, during the other half the other side, and at each half-period, their edge..
- Q: This also depends on the inclination of Atys with respect to its orbital plane, right?
- A: Yes, the latter is about 20°.
Sagaritis, like the Moon seen from the Earth, should also have its phases: full, dark, rising, falling, etc. In the night zone, one would often see flashes of lightning and at the poles, huge aurora borealis. In the illuminated zone of Sagaritis we would see curling and unwinding wisps (similar to the one we see on the surface of Jupiter and Saturn... as long as we get close to them). Its rings would always shine, whether it is black or not, but sometimes a part of it would be hidden by the shadow of its mass. Conversely, the shadow of the rings would sometimes be projected on Sagaritis. Finally, as Cybele could pass behind Sagaritis, one would sometimes observe an eclipse.
To continue the comparison with our solar system, I specify that Atys, satellite of Sagaritis, is of a size similar to Mars and has a gravity slightly lower than 1G.
- Q: Does this mean that the proportion of hidden territory is huge?
- A: Yes. *smile* That leaves room for lots of creation!
- Q: Ah, how about that! Have our homins have any idea of sa taille ?
- A: No, the homins don't think it's that big. On the other hand, Oflovak did achieve some things.
- Q: Are homins able to measure great distances with precision?
- A: Yes, thanks to the fixed stars. But especially the distances along the parallels. For medium distances, it is more difficult, because the observable displacement of the star is not sufficient.
The “Red Moon”, as for it, is also called “Amber Moon”, or “Karavan Moon”, “Kami Moon”, “Tryton Moon”. It is always full (no phases) and its size is variable. If it were "correct" in game, it would only be visible at night for three quarters of each cycle, since for the remaining quarter it would be positioned above the other side of Atys.
- Q: It's moving away and getting closer?
- A: Yes.
- Q: Does it have a particular orbit?
- A: It is in the same plane as Atys, but different from it.
- Q: More elliptical?
- A: Yes, and there's a kind of chase between the two.
I'm not going to tell you exactly what the nature of this celestial body is. Just know that it is neither rock nor ice. In fact its mass is very low compared to that of Atys. Perhaps the trytonists would know another name for it. A name that would sound like “Ryzom”. But I'm starting to talk too much...
- Q: You still need to explain how it radiates its own light.
- A: There is a kind of energy that emanates from it, but not enough to be seen by day.
- Q: Oh OK: it's always there, even in daylight, but then not bright enough to be seen?
- A: Yes, except when it is behind Atys. During a cycle, it rises and sets. But when it is at the zenith, it seems for several months to move in slow motion, it is very strange!
To finish with astronomy, a word about the starlit sky. If it were "correctly represented" in game, it would not rotate during the night, but much more slowly, on a cycle. In addition to shooting stars, we would sometimes see bright objects moving quickly and flashing.
- Q: When I look at the moon, there seems to be a light shining directly below it... does anyone know what it is? Do we know the source?
- A: No. I think it's like a not quite properly realized effect. In fact it's a mistake: the light on Atys comes from the horizon like on Earth. In the same way, when the day comes, the light should not come from the horizon but from the luminary whose brightness increases progressively.
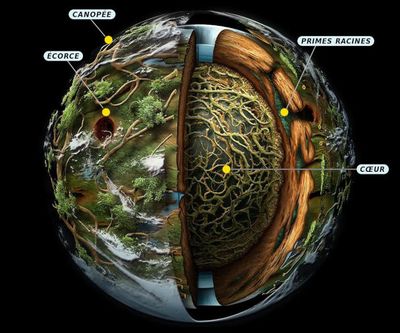
The Canopy
I would now like to go down a notch in altitude and say a few words about the Canopy. Its branches run between 1 and 2 kilometers in altitude and are between 200 and 500 meters thick. If we were to stick to the "artist's view" of the planet mentioned above, they would be at least 300 km thick! It would be night below.
- Q: Have homins ever been on the Canopy?
- A: Climbing the start of a Canopy root would be possible in principle, if it is not too steep. But, assuming one reaches the top of the Canopy, there would be health complications!
The surface of Atys
To represent the surface of Atys, imagine the same thing as the Canopy, but placed on the ground. It is made of compartments, and these compartments draw like a map of the game.
- Q: Is the “ground” of Atys roots? Or is it something between roots? And if so, what is it?
- A: The subsoil of Atys is composed of many layers of roots on top of each other.
- Q: So the roots form the edges and bottoms of kind of compartments?
- A: Yes, and each compartment fills with debris. And the last layer is at the top: that' s the canopy.
- Q: We are on a root mat with sawdust between the roots to give an illusion of continuity?
- A: Yes. But in the Old Lands there are larger compartments. The New Lands, around the Nexus, is special.
- Q: What do you mean? What's so special about it?
- A: The fact of having several different biotopes in a very small area, and small extents.
- Q: The plants we see on Atys, are they epiphytes of these roots that form the compartments or are they connected to them?
- A: They are epiphytes except for the crolices (which are indeed connected to them).
- Q: Why has no explorer tried to see what lies beyond the horizon? Beyond the cliffs? Fear of not being able to be relieved by the Powers?
- A: Yes, because the New Lands are an El Dorado, since the Powers offer there resurrection for all. This was not the case in the Old Lands, before the Great Swarming.
The years of Jena (JY)
As you know, in the calendar we have cycles, and Jena years and there is an equivalence between the Jena year and the earth year. But not only: in fact, to say more, the current date 2614, is indeed the future of our 2021.
- Q: Atys is the future of the Earth ! Did I understand correctly?
- A: The story is set in the future of the Earth, yes. But that doesn't mean that Atys is the Earth. That's why the fantasy approach of Ryzom hides a SF reality.